
Like activities and the other components, services run in the main thread of the application process.Each service extends the Service base class. For example, a service might play background music as the user attends to other matters, or it might fetch data over the network or calculate something and provide the result to activities that need it. A service doesn't have a visual user interface, but rather runs in the background for an indefinite period of time.The content view is the View object at the root of the hierarchy. A view hierarchy is placed within an activity's window by the tContentView()method.Android has a number of ready-made views that you can use - including buttons, text fields, scroll bars, menu items, check boxes, and more. For example, a view might display a small image and initiate an action when the user taps that image.
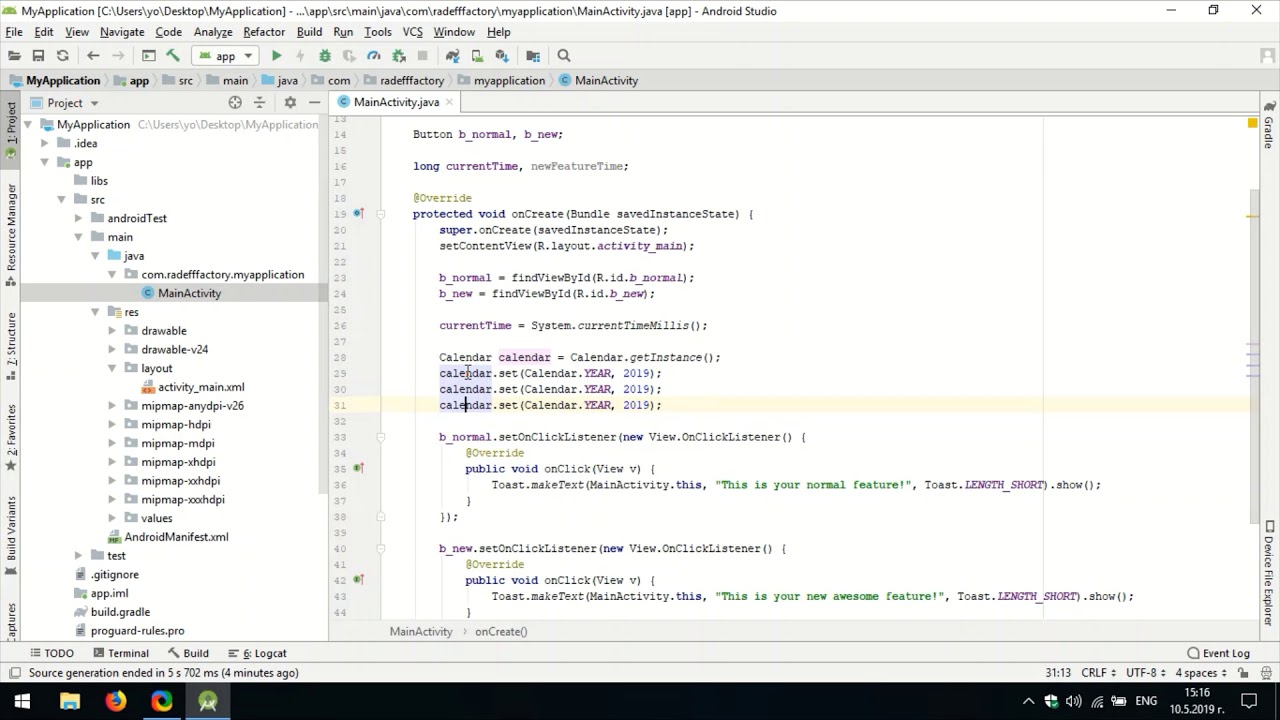
Thus, views are where the activity's interaction with the user takes place.Leaf views (those at the bottom of the hierarchy) draw in the rectangles they control and respond to user actions directed at that space.Parent views contain and organize the layout of their children.Each view controls a particular rectangular space within the window. The visual content of the window is provided by a hierarchy of views - objects derived from the base VIEWclass.Each one is implemented as a subclass of the Activitybase class.Though they work together to form a cohesive user interface, each activity is independent of the others. A text messaging application might have one activity that shows a list of contacts to send messages to, a second activity to write the message to the chosen contact, and other activities to review old messages or change settings.An activity presents a visual user interface for one focused endeavour the user can undertake.Unlike applications on most other systems, Android applications don't have a single entry point for everything in the application (no main() function, for example).
Android Tutorial Presented By: Rajesh Kumar Behera


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
